The Bombay High Court has dismissed a mosque's plea for loudspeakers, ruling they are "not integral" to religion. The verdict backs a statewide crackdown on noise pollution.
 Suneel Patel
Suneel Patel
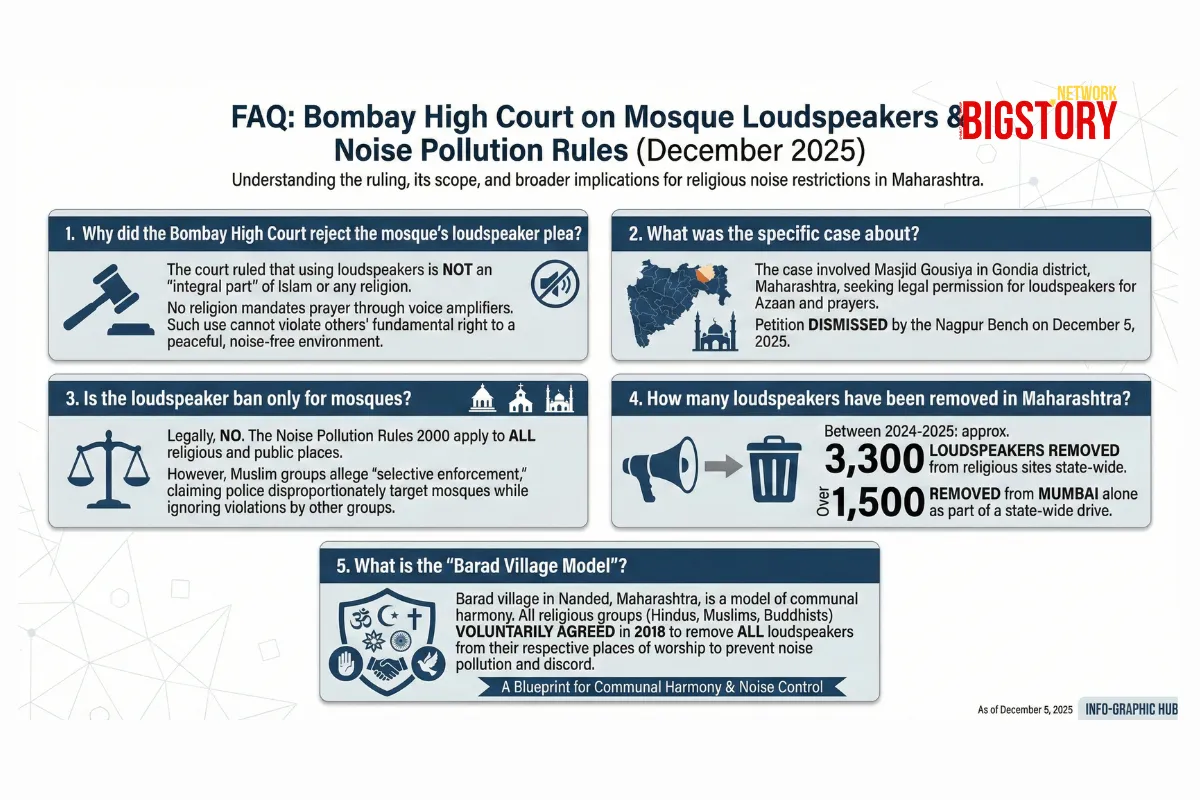
The Bombay High Court's Nagpur Bench has dismissed a petition by Masjid Gousiya in Gondia district, ruling on December 5, 2025, that "loudspeakers are not integral to practicing any religion." Citing the fundamental right of citizens to a noise-free environment, the court rejected the mosque's request for permission to use amplifiers for prayers. This judgment validates the ongoing statewide crackdown in Maharashtra, where authorities have already removed over 3,300 loudspeakers from religious sites in the past year, intensifying the debate over the balance between religious freedom and civic order.
The ruling follows a contentious year. Since July 2024, the Maharashtra government, led by CM Devendra Fadnavis, has enforced strict noise pollution norms, leading to the removal of thousands of loudspeakers, particularly from mosques in Mumbai. In July 2025, five Mumbai mosques petitioned the High Court alleging "hostile discrimination," claiming police were targeting them while ignoring high-decibel noise from temples and event halls. The court's latest decision leans heavily on the Noise Pollution Rules 2000 and prior Supreme Court precedents, reinforcing that religious practice cannot override public nuisance laws.
While the headlines focus on the "Mosque vs. State" narrative, the deeper story is the "Enforcement Gap." Data shows over 3,300 loudspeakers removed, but transparency on the religious breakdown of these removals is missing. Are temple bells and festival DJs subject to the same decibel meters as the morning Azaan? The court's ruling is legally sound on paper, but its application on the ground risks becoming a tool of majoritarian assertion if enforcement remains opaque. The real test of this judgment isn't whether it silences the Azaan, but whether it silences all noise pollution equally.
This verdict arms the state with judicial backing to escalate its removal drive. It forces mosques to explore alternatives—like app-based notifications for prayer times—potentially modernizing a centuries-old tradition. However, it also deepens communal fault lines. If the perception of "selective justice" persists, it could fuel unrest. Conversely, the "Barad Village Model"—where communities voluntarily removed all loudspeakers—shows a path to harmony that courts and police batons cannot achieve.
If God can hear a silent prayer, why does faith need a amplifier to reach the faithful?
Why did the Bombay High Court reject the mosque's loudspeaker plea? The court ruled that using loudspeakers is not an "integral part" of Islam or any religion. It emphasized that no religion mandates prayer through voice amplifiers and that such use cannot violate others' fundamental right to a peaceful, noise-free environment.
What was the specific case about? The case involved Masjid Gousiya in Gondia district, Maharashtra, which sought legal permission to use loudspeakers for Azaan and prayers. The petition was dismissed by the Nagpur Bench on December 5, 2025.
Is the loudspeaker ban only for mosques? Legally, no. The Noise Pollution Rules 2000 apply to all religious and public places, including temples, churches, and event halls. However, Muslim groups allege "selective enforcement," claiming police are disproportionately targeting mosques while ignoring violations by other groups.
How many loudspeakers have been removed in Maharashtra? Between 2024 and 2025, authorities in Maharashtra have removed approximately 3,300 loudspeakers from religious sites, with over 1,500 removed from Mumbai alone, as part of a state-wide drive.
What is the "Barad Village Model"? Barad village in Nanded, Maharashtra, is a model of communal harmony where all religious groups (Hindus, Muslims, Buddhists) voluntarily agreed in 2018 to remove all loudspeakers from their respective places of worship to prevent noise pollution and communal discord.
News Coverage
Research & Analysis






Sign up for the Daily newsletter to get your biggest stories, handpicked for you each day.
 Trending Now! in last 24hrs
Trending Now! in last 24hrs